Cysts are common occurrences on the skin, and when they form on the arm, they often present as a notable lump or bump. These growths can be found just under the skin or deeper in the arm’s tissue. While many people might first encounter a cyst on their arm with a touch of concern, it’s worth noting that cysts are typically benign and rarely cause serious issues.
Understanding the nature of cysts is essential for proper management and treatment. A cyst on the arm is usually a closed capsule or sac-like structure, potentially filled with liquid, semi-solid, or gaseous material. It’s not uncommon for individuals to discover them during a routine self-exam or accidentally while doing daily activities.
Key Takeaways
- A cyst is a noncancerous growth that can appear as a lump on the arm.
- Proper diagnosis of a cyst is critical for determining the appropriate treatment.
- Most arm cysts are benign, but monitoring for changes is essential to prevent complications.
Understanding Cysts
In discussing cysts on the arm or any other area, it’s imperative to highlight that cysts are noncancerous, closed pockets of tissue that can be filled with fluid, pus, or other material. They often develop naturally and can appear anywhere on the body.
Types of Cysts
When it comes to classifying cysts, there are several types one might encounter. I can outline some of the most common types below:
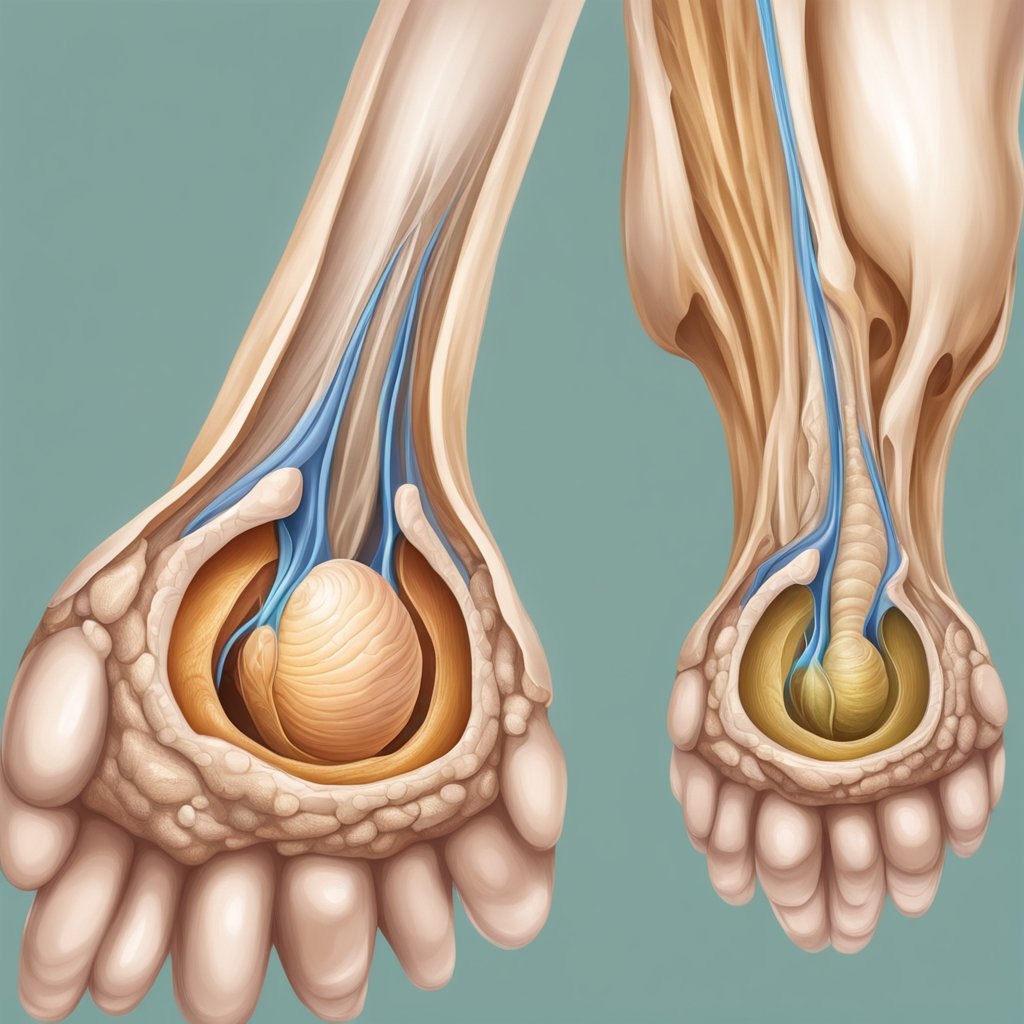
- Ganglion cysts: Typically found on the wrist, these cysts are filled with a jellylike fluid.
- Epidermoid cysts: Often occurring on the face, neck, or torso, these cysts arise from the skin and are filled with keratin.
- Sebaceous cysts: These occur as a result of blocked sebaceous glands, typically found on the face, neck, or trunk.
- Lipomas: Although not strictly a cyst, lipomas are soft, fatty lumps that grow under the skin and are worth mentioning.
- Skin cysts: A general category that includes various cysts occurring on the skin which can sometimes also be found on the arms.
Common Locations
Cysts can manifest in numerous locations across the body, not just the arm. Here’s a concise list of some common areas where cysts might occur, often depending on their type:
- Wrist or Hand: Preferring joint or tendon areas, ganglion cysts are most commonly seen here.
- Face, Neck, and Torso: Epidermoid and sebaceous cysts are frequently located in these regions, associated with hair follicles and skin glands.
- Arms and Upper Torso: Skin cysts of various types can appear on the arms, providing a broad category that encompasses multiple specific kinds of cysts.
Understanding that cysts vary by type and location is critical for recognizing and addressing them appropriately. Each type has its characteristics and preferred locations, which can be crucial for identification and management.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors for cysts on the arm can help in prevention and treatment. Two leading components play a role in cyst development: the initiating trigger and personal susceptibility.
Causes of Cysts
Cysts can form for various reasons, but common causes include:
- Blocked Oil Glands: My skin’s oil glands can become clogged, leading to the formation of cysts.
- Inflammation: Inflammation in hair follicles or skin tissue often contributes to cyst development.
- Injury: An injury to my arm might cause a cyst to form as a protective response.
- Infection: If an infection occurs deep within my skin, a pus-filled cyst may emerge.
Risk Factors for Development
Certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing cysts:
- Genetics: My family history plays a role. If my relatives are prone to cysts, I may be more likely to develop them.
- Age and Sex: Typically, adults are more affected by cysts. Males face a higher risk of developing sebaceous cysts.
- Skin Conditions: Individuals with acne or other skin conditions are at a heightened risk for cysts, as these can disturb the hair follicles or oil glands.
By staying vigilant about these risk factors, I can better understand and manage the potential for cyst formation.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
When I notice an unusual lump on my arm, it’s crucial for me to recognize the symptoms and seek appropriate diagnosis to understand the nature of the cyst.
Identifying Symptoms
The most common symptom I might observe is a skin-colored bump. It could be tender to touch and may cause discomfort or pain when I apply pressure. Swelling around the area might also be present. These symptoms often lead me to consider medical evaluation:
- Visible Lump: A noticeable bump beneath the skin that’s typically round.
- Discomfort: Varying levels of pain or tenderness when the cyst is pressed.
- Skin Changes: The skin over the cyst may appear normal or slightly stretched; sometimes reddened if inflamed.
Diagnostic Procedures
Scheduling a visit with a doctor is the first step I take for a diagnosis. Here’s what the diagnostic process might involve:
- Physical Examination: A thorough check of the affected area by a dermatologist.
- Medical History Review: Discussing any relevant personal or family skin conditions.
Following the initial assessment, further diagnostic tests could include:
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Ultrasound | To visualize the cyst’s interior and rule out solid growths. |
| Fine-needle Aspiration | Extracting fluid from the cyst for lab analysis. |
| Biopsy | Taking a small tissue sample if the cyst appears atypical. |
If these procedures indicate a benign cyst, often there may be no need for immediate treatment unless I’m experiencing significant pain or discomfort.
Treatment Options
When considering treatment options for a cyst on the arm, it’s crucial to understand that the approach can range from conservative home remedies to medical and surgical interventions, depending on the cyst’s characteristics and symptoms.
Home Care and Remedies
For cysts that are not infected or causing significant discomfort, I may recommend simple home care strategies. Applying warm compresses can help alleviate pain and promote drainage if the cyst becomes inflamed or tender. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen, can also be used to manage discomfort.
- Warm Compresses: Apply to the cyst for 10-15 minutes several times a day.
- Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen, as needed, following the dosage instructions on the packaging.
Medical Interventions
If home remedies do not sufficiently address the issue, I may prescribe medications or perform an in-office procedure. Antibiotics are used in cases where the cyst is infected or if there’s a risk of infection. In some instances, the cyst can be aspirated, which involves puncturing and draining the fluid from the cyst.
- Antibiotics: For infected cysts.
- Aspiration: A needle is used to drain the cyst.
Surgical Procedures
Surgery might be required if the cyst is recurrent, causes persistent pain, or is suspected to be cancerous. I perform a minor surgical procedure to remove the entire cyst to prevent recurrence. This is done under local anesthesia, and post-surgery, instructions are provided to ensure proper healing.
- Surgical Removal: Excision of the cyst under local anesthesia.
- Post-Surgery Care: Includes wound care and follow-up appointments for suture removal or to monitor healing.
Potential Complications
In discussing cysts on the arm, it’s paramount to recognize that while many are benign, there are circumstances when they may lead to further health concerns. I’ll outline when medical evaluation is advised and explain possible complications.
When to See a Doctor
- Persistent Growth: If I notice the cyst growing consistently, it may be time for a medical review.
- Discomfort or Pain: Should the cyst cause significant discomfort or pain, which could indicate underlying issues, seeking medical advice is necessary.
- Visual Changes: Any changes in color or shape might require a doctor’s examination to rule out malignancy.
- Compromised Mobility: If the location of the cyst hinders my joint movement or daily activities, professional assessment is important.
Possible Complications
- Infection: If the cyst becomes red, warm, and painful, it might be infected. Signs of pus or drainage would necessitate immediate medical attention, preferably by visiting an emergency room (ER).
- Rupture: A ruptured cyst can lead to acute inflammation and sometimes infection. In such a case, professional intervention is required to manage the symptoms and prevent further complications.
- Swelling: Significant swelling around a cyst may suggest an inflammatory response, which could also point to infection or complications requiring medical evaluation.
- Malignancy Concerns: While rare, a cyst on the arm that exhibits rapid growth, irregular borders, or an unusual color might prompt a biopsy or further tests for skin cancer assessment.
When considering these potential issues, I adhere to the guideline of erring on the side of caution by consulting healthcare professionals if any worrisome signs arise.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, I cover the most common inquiries concerning lumps on the arm, focusing on causes, differentiation, types, symptoms, self-resolution, and when to seek medical advice.
What could be the cause of a lump developing on the forearm?
The emergence of a lump on the forearm can be attributed to various factors, such as cyst formation, infections, or benign tumors like lipomas. Trauma or injury can also result in lumpy swelling if there is localized collection of fluid or blood.
How can one differentiate between a cyst and other types of lumps?
To distinguish a cyst from other lumps, I look for characteristics such as a round shape, a defined edge, and a fluctuant feel, which may indicate a fluid-filled sac typical of cysts. Other lumps may be hard, immovable, and could arise from structures deep under the skin, differing from the usual presentation of a cyst.
Are there various types of cysts that can appear on the arm?
Yes, there are multiple kinds of cysts that may develop on the arm. I often see epidermoid cysts, which stem from the skin’s surface, or ganglion cysts, which are typically linked to joints and tendons. Both types manifest differently in appearance and texture.
What symptoms might accompany a lump on the arm that suggest it’s a cyst?
When a lump on the arm accompanies symptoms like a non-painful, smooth surface that may feel filled with liquid, this suggests a cyst. Some cysts, such as sebaceous ones, might also have a white or yellowish hue, indicating the presence of trapped oils or other substances.
Can a cyst on the arm resolve on its own without medical intervention?
It’s possible for a cyst on the arm to resolve spontaneously, especially if it’s small and not infected. Some cysts might shrink over time or remain unchanged. However, persistent or bothersome cysts likely require medical intervention for removal or drainage.
When should someone be concerned about a lump on their arm and seek medical advice?
I recommend seeking medical advice for a lump on the arm if it’s rapidly growing, painful, red, or hot to the touch, suggesting an infection or more serious condition. Additionally, lumps that persist or cause discomfort should be evaluated by a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.